
Construction Safety Statistics 2025: The True Cost of Contractor Non-Compliance
Construction remains one of the UK’s most hazardous industries, with fatal injury rates significantly higher
Health and Safety Software » Health and Safety Software News » Health and Safety » Working with Blood Products
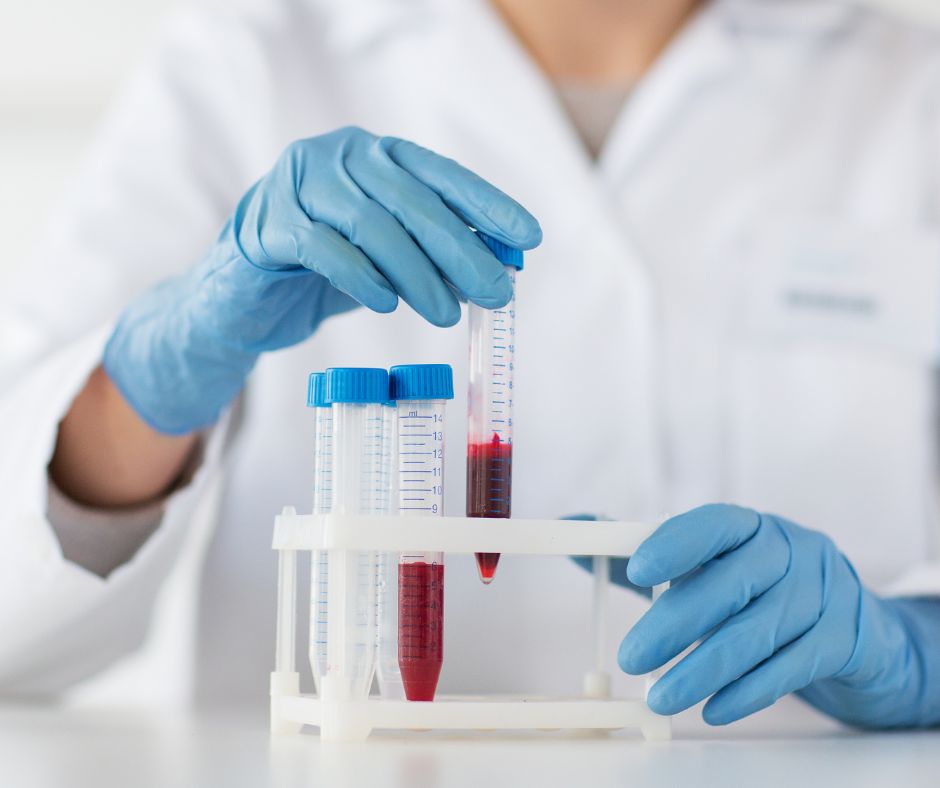

Blood-borne pathogens are viruses or bacteria that can be transmitted through contact with blood or other bodily fluids. They can cause serious and life-threatening illnesses.
Exposure to blood-borne pathogens can occur in several ways, including:
Control measures
In addition to the control measures listed above, there are several other things that laboratory workers can do to reduce their risk of exposure to blood-borne pathogens, such as:
Specific risks and control measures for working with blood products in a lab
In addition to the general risks and control measures listed above, there are also some specific risks and control measures that need to be considered when working with blood products in a lab.
One of the biggest risks is exposure to blood-borne pathogens. Blood-borne pathogens can cause serious and life-threatening illnesses. To reduce the risk of exposure to blood-borne pathogens, laboratory workers should always wear PPE when handling blood products. PPE should include gloves, gowns, goggles, and face masks.
Another risk is exposure to allergens. Some people are allergic to blood products. Laboratory workers should be aware of their own allergies and avoid handling blood products that they are allergic to. If a worker is exposed to a blood product that they are allergic to, they should seek medical attention immediately.
Finally, there is also a risk of exposure to chemicals. Some blood products are treated with chemicals to prevent them from clotting or to preserve them. Laboratory workers should be aware of the chemicals that are used in the blood products they are working with and take precautions to avoid exposure.
Specific control measures for working with blood products in a lab include:
Working with blood products in a lab can be dangerous if proper safety precautions are not taken. By following the control measures listed above, laboratory workers can reduce their risk of exposure to blood-borne pathogens, allergens, and chemicals.
Additional tips for working safely with blood products in a lab
The iProtectU health and safety software provides:
Arrange your demonstration
Let us show you how we can transform your health and safety, risk and compliance management
Please choose a date and time for your demo. We look forward to meeting with you.

Construction remains one of the UK’s most hazardous industries, with fatal injury rates significantly higher
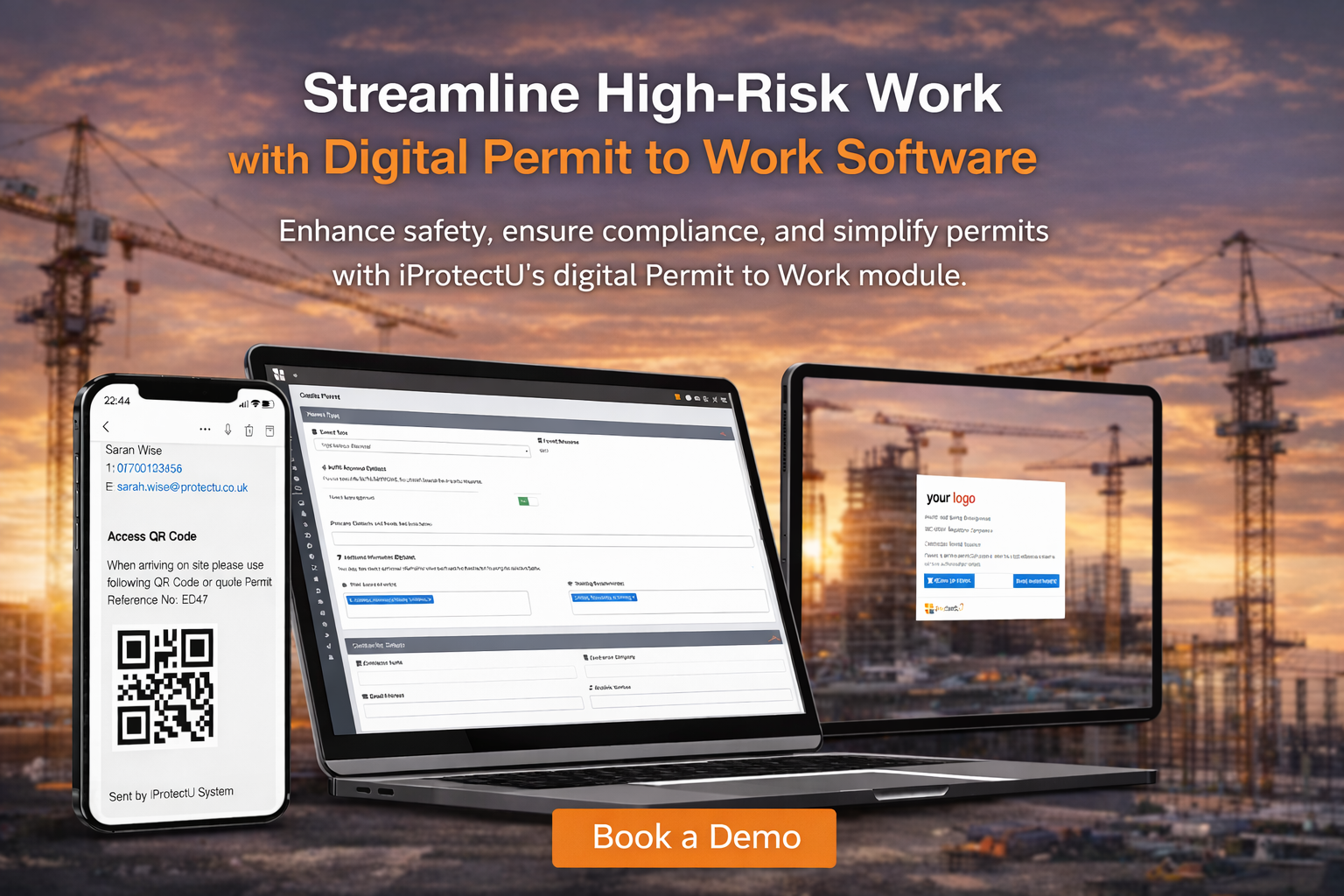
Permit to Work software helps organisations manage high-risk tasks safely and compliantly. Discover how iProtectU’s

Achieving ISO 45001 doesn’t need to be complex or resource-heavy. The real challenge isn’t understanding

Discover how eLearning and training management software helps organisations deliver, track and optimise workplace safety

As we step into 2026, it’s time to embrace a smarter approach to safety. Discover

Ho ho hold on – before you climb that ladder to hang the fairy lights…