
Is Your Organisation Ready for Today’s Travel Risks? Protect Your Travellers in a Changing World
Global business travel is growing again, with spending expected to reach $1.57 trillion in 2025,
Health and Safety Software » Health and Safety Software News » Standard Operating Procedures » Steps involved in the Development of a Safe System of Work

They are important for protecting workers from injury and illness, and for ensuring that work is carried out in a safe and efficient manner.
There are five key steps to developing a safe system of work:
Step 1: Assess the task
The first step is to assess the task that needs to be done. This involves identifying all the steps involved in the task, as well as the equipment and materials that will be used. It is also important to consider the people who will be carrying out the task, and their level of skill and experience.
Step 2: Identify the hazards
The next step is to identify any hazards that may be present. Hazards can be anything that has the potential to cause harm, such as physical hazards (e.g., sharp objects, moving machinery), chemical hazards (e.g., toxic substances, fumes), biological hazards (e.g., bacteria, viruses), and ergonomic hazards (e.g., repetitive tasks, awkward postures).
Step 3: Define safe methods
Once the hazards have been identified, the next step is to define safe methods for carrying out the task. This involves identifying ways to eliminate or minimise the risks associated with each hazard. For example, if there is a risk of being struck by falling objects, a safe method may involve wearing a hard hat and working in an area where there is overhead protection.
Step 4: Implement the system
Once the safe methods have been defined, the next step is to implement the system. This involves training workers on the safe methods and providing them with the necessary equipment and resources. It is also important to communicate the system to all relevant stakeholders, such as contractors and visitors.
Step 5: Monitor the system
The final step is to monitor the system to ensure that it is effective and that workers are following the safe methods. This can be done through observation, audits, and feedback from workers. It is vital to review the system regularly to ensure that it is up-to-date and that it reflects any changes in the workplace or in the tasks that are being carried out.
Tips for developing a safe system of work
In addition to the five steps outlined above, there are several other things to consider when developing a safe system of work. These include:
The iProtectU health and safety software provides:
Arrange your demonstration
Let us show you how we can transform your health and safety, risk and compliance management
Please choose a date and time for your demo. We look forward to meeting with you.

Global business travel is growing again, with spending expected to reach $1.57 trillion in 2025,

Construction remains one of the UK’s most hazardous industries, with fatal injury rates significantly higher
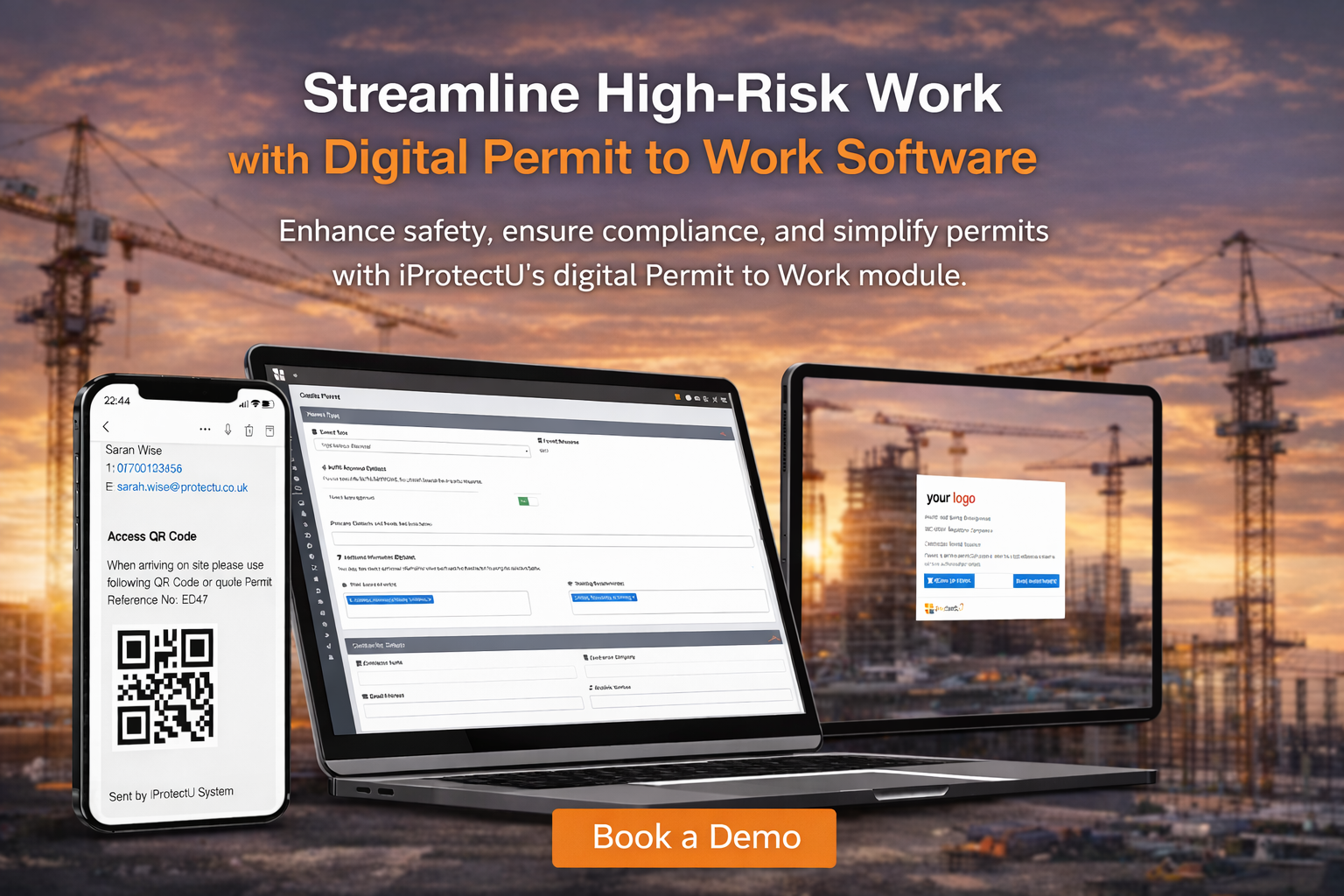
Permit to Work software helps organisations manage high-risk tasks safely and compliantly. Discover how iProtectU’s

Achieving ISO 45001 doesn’t need to be complex or resource-heavy. The real challenge isn’t understanding

Discover how eLearning and training management software helps organisations deliver, track and optimise workplace safety

As we step into 2026, it’s time to embrace a smarter approach to safety. Discover